Data Classification Tutorial
Apache Eagle data classification feature provides the ability to classify data with different levels of sensitivity. Currently this feature is available ONLY for applications monitoring HDFS, Hive1 and HBase2. For example, HdfsAuditLog, HiveQueryLog and HBaseSecurityLog.
The main content of this page are
- Cluster Connection
- Data Classification
Cluster Connection
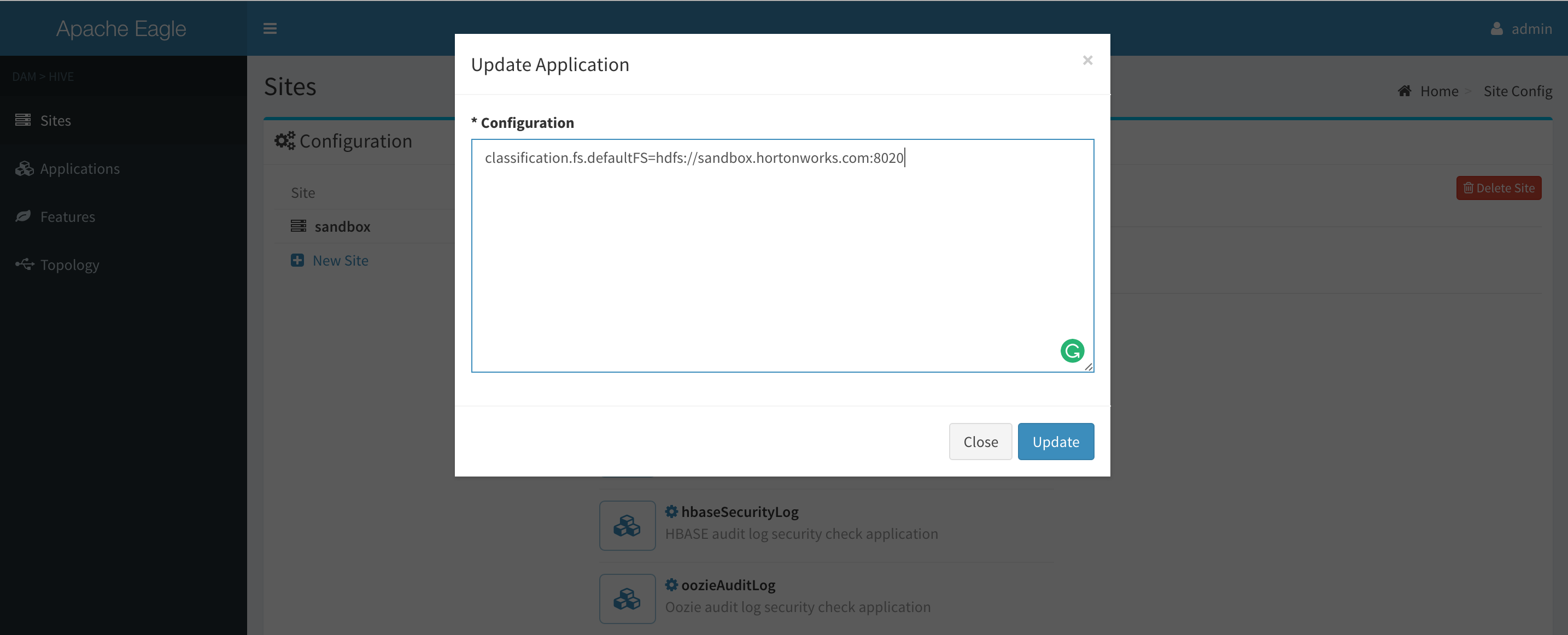
Here we give example configurations for HDFS, HBASE, and Hive. Suppose the cluster to monitor is Hortonwork sandbox. This configuration locates at the admin management page.
-
HDFS
-
Base case
You may configure the default path for Apache Hadoop clients to connect remote hdfs namenode.
classification.fs.defaultFS=hdfs://sandbox.hortonworks.com:8020 -
HA case
Basically, you point your fs.defaultFS at your nameservice and let the client know how its configured (the backing namenodes) and how to fail over between them under the HA mode
classification.fs.defaultFS=hdfs://nameservice1 classification.dfs.nameservices=nameservice1 classification.dfs.ha.namenodes.nameservice1=namenode1,namenode2 classification.dfs.namenode.rpc-address.nameservice1.namenode1=hadoopnamenode01:8020 classification.dfs.namenode.rpc-address.nameservice1.namenode2=hadoopnamenode02:8020 classification.dfs.client.failover.proxy.provider.nameservice1=org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.ha.ConfiguredFailoverProxyProvider -
Kerberos-secured cluster
For Kerberos-secured cluster, you need to get a keytab file and the principal from your admin, and configure “eagle.keytab.file” and “eagle.kerberos.principal” to authenticate its access.
classification.eagle.keytab.file=/EAGLE-HOME/.keytab/eagle.keytab classification.eagle.kerberos.principal=eagle@SOMEWHERE.COMIf there is an exception about “invalid server principal name”, you may need to check the DNS resolver, or the data transfer , such as “dfs.encrypt.data.transfer”, “dfs.encrypt.data.transfer.algorithm”, “dfs.trustedchannel.resolver.class”, “dfs.datatransfer.client.encrypt”.
-
- Hive
-
Basic
classification.accessType=metastoredb_jdbc classification.password=hive classification.user=hive classification.jdbcDriverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver classification.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql://sandbox.hortonworks.com/hive?createDatabaseIfNotExist=true
-
-
HBase
-
Basic case
You need to sett “hbase.zookeeper.quorum”:”localhost” property and “hbase.zookeeper.property.clientPort” property.
classification.hbase.zookeeper.property.clientPort=2181 classification.hbase.zookeeper.quorum=localhost -
Kerberos-secured cluster
According to your environment, you can add or remove some of the following properties. Here is the reference.
classification.hbase.zookeeper.property.clientPort=2181 classification.hbase.zookeeper.quorum=localhost classification.hbase.security.authentication=kerberos classification.hbase.master.kerberos.principal=hadoop/_HOST@EXAMPLE.COM classification.zookeeper.znode.parent=/hbase classification.eagle.keytab.file=/EAGLE-HOME/.keytab/eagle.keytab classification.eagle.kerberos.principal=eagle@EXAMPLE.COM
-
Any questions on the Kerberos configuration in Eagle, please first check FAQ
Data Classification
After the configuration is updated, we can go back to the classification page on Eagle UI. Here we take HdfsAuditLog as an example to explain how to classify data and how to monitor sensitive data in Eagle.
Part 1: Sensitivity Edit
-
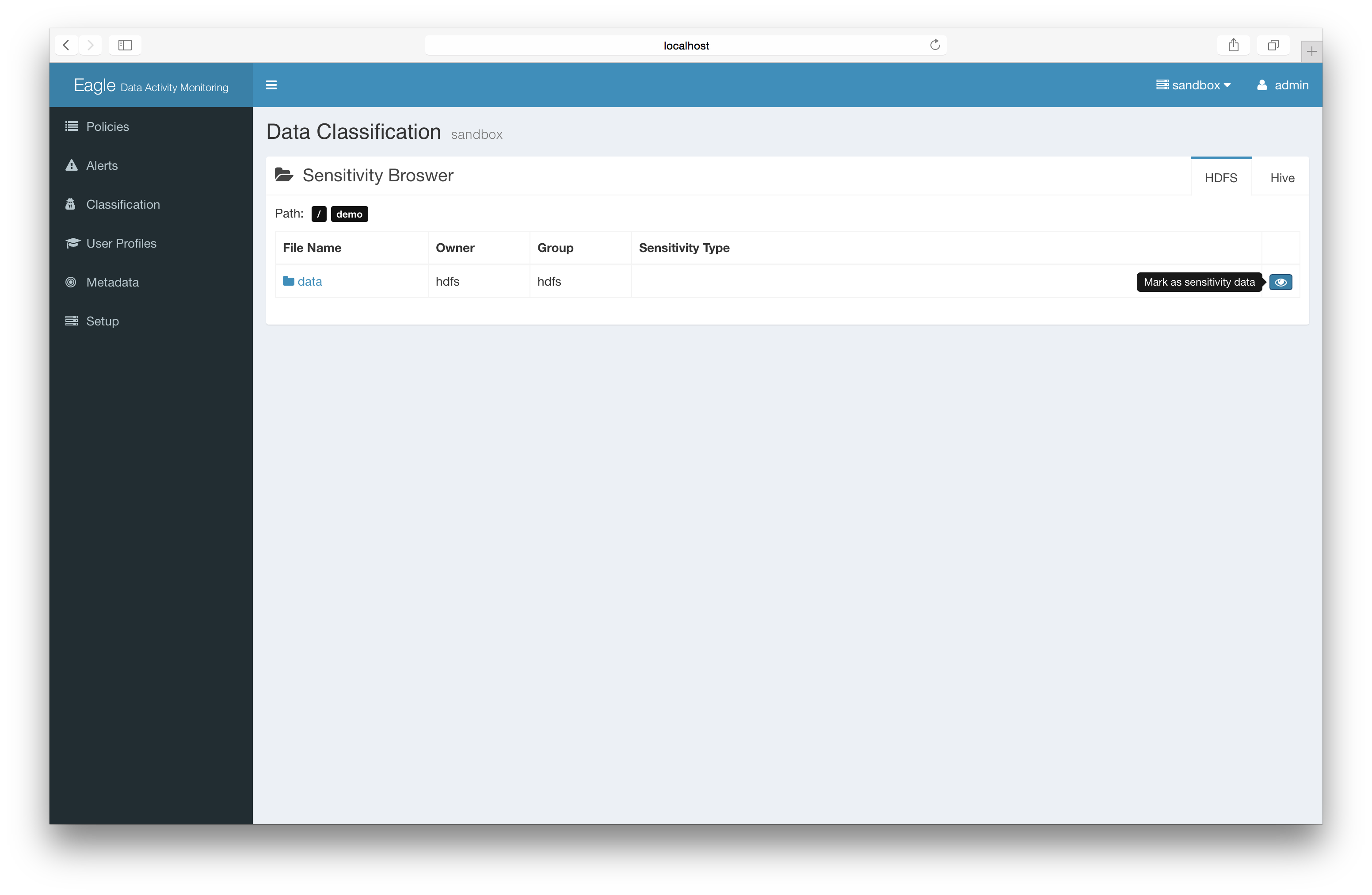
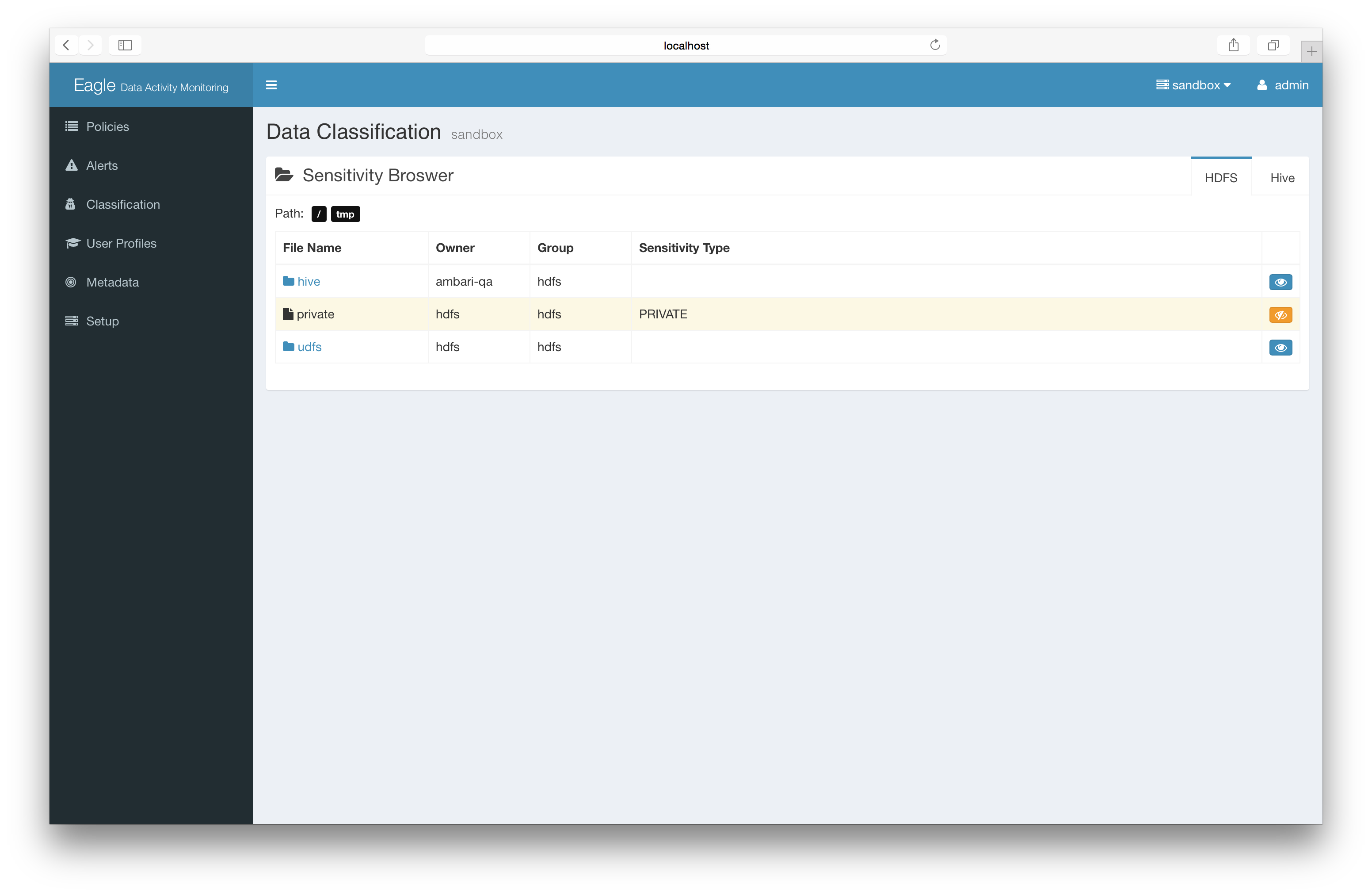
add the sensitive mark to files/directories.
-
Basic: Label sensitivity files directly (recommended)
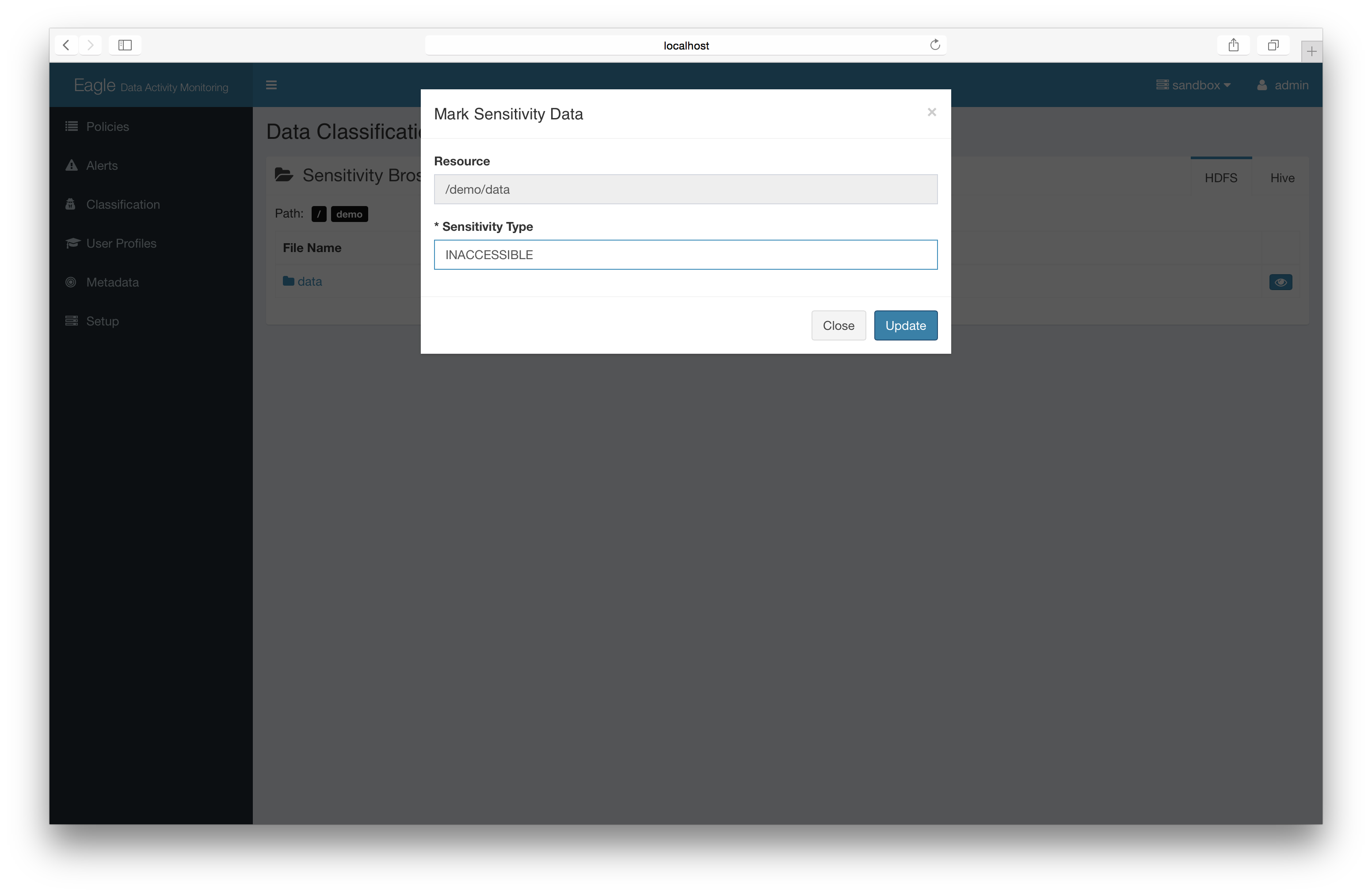
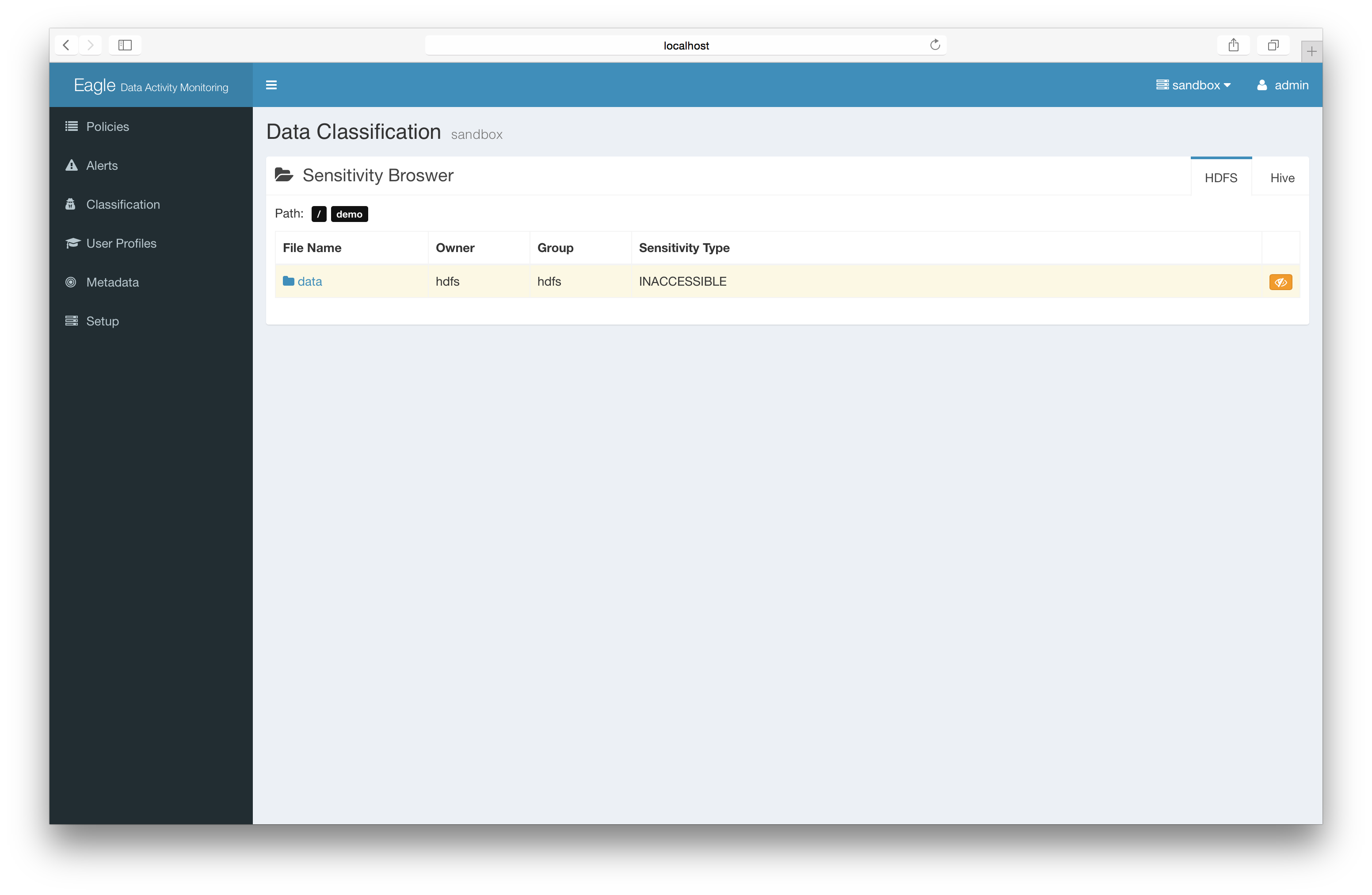
-
Advanced: Import json file/content
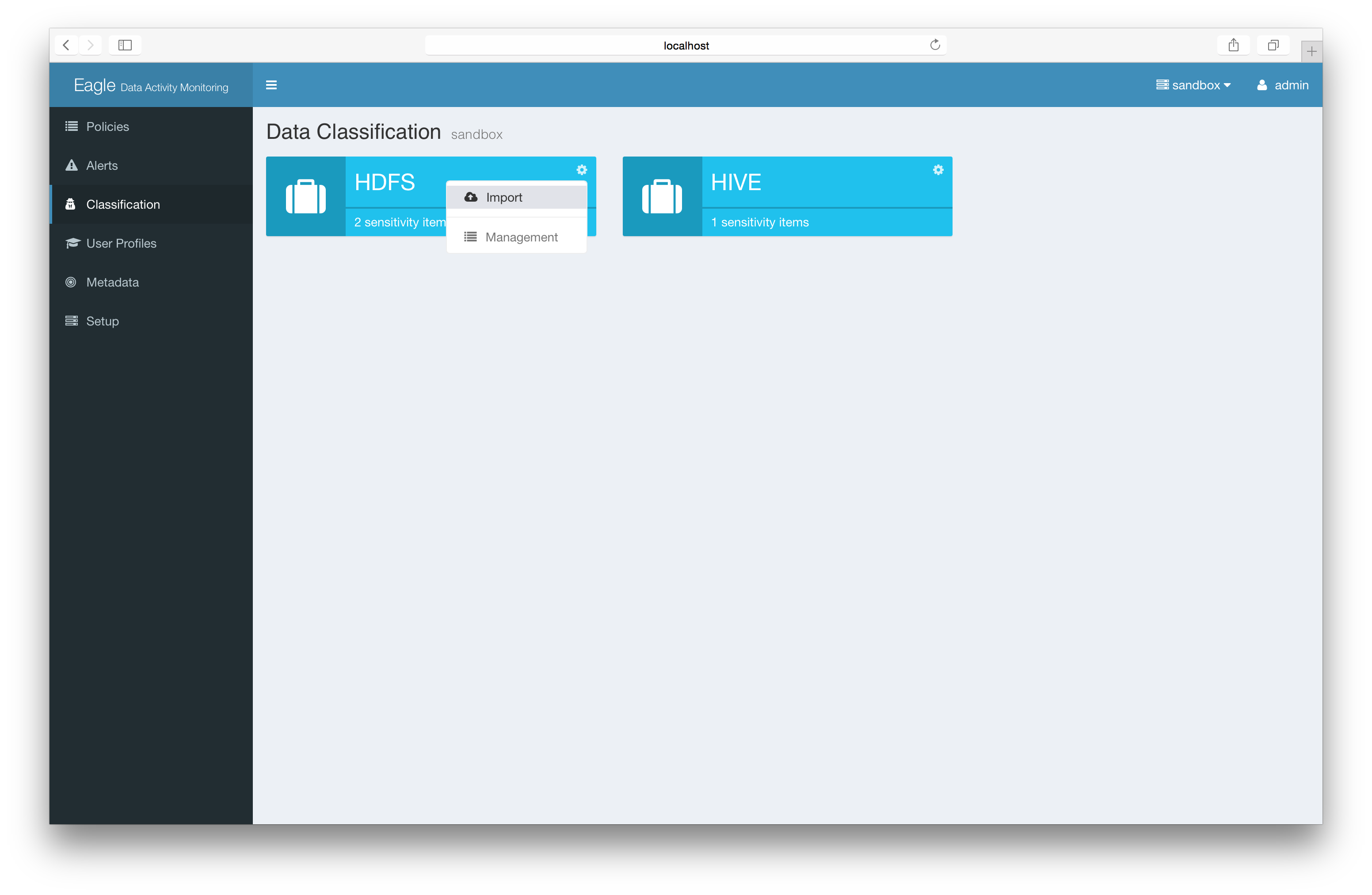
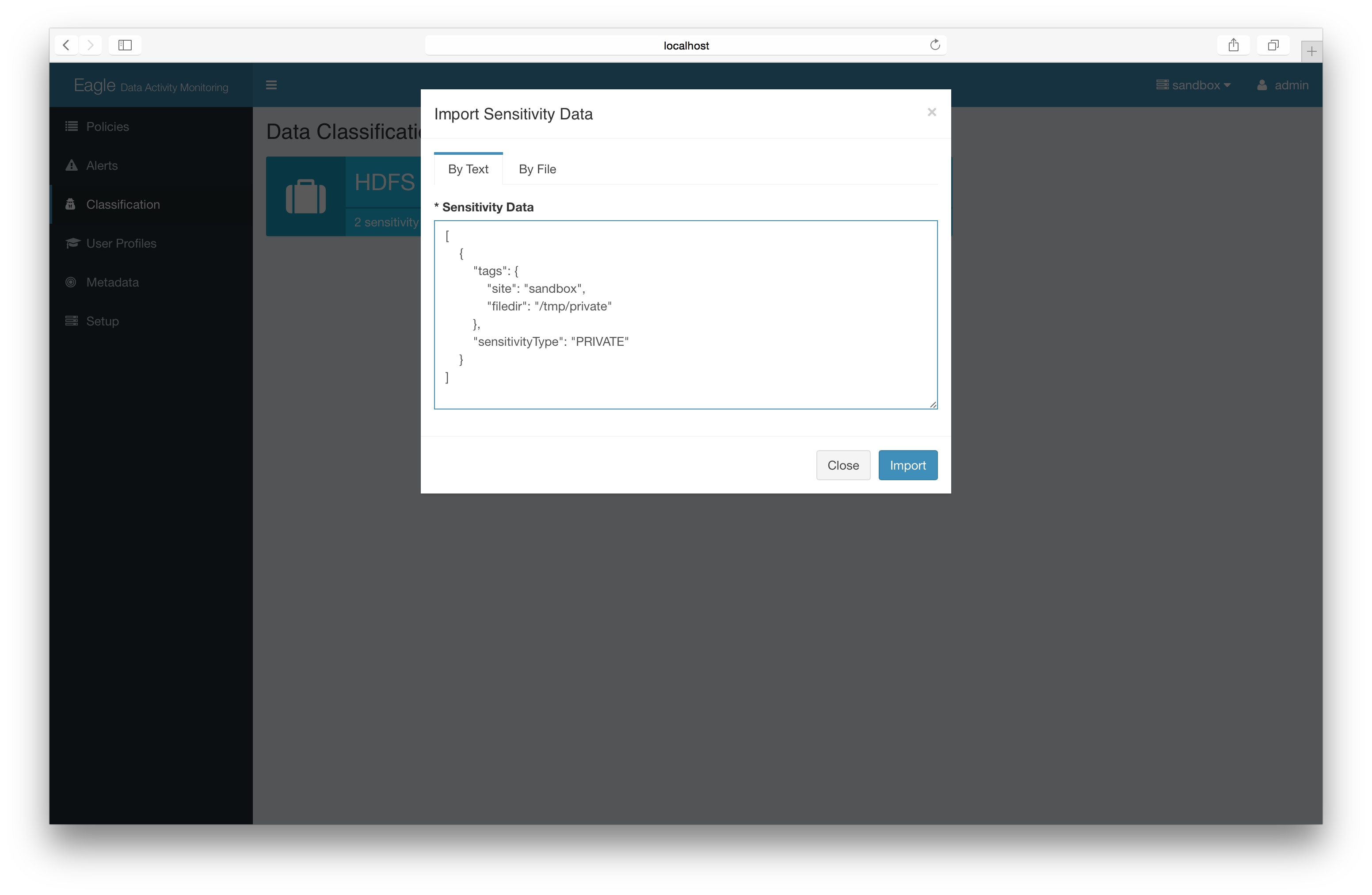
-
-
remove sensitive mark on files/directories
-
Basic: remove label directly
-
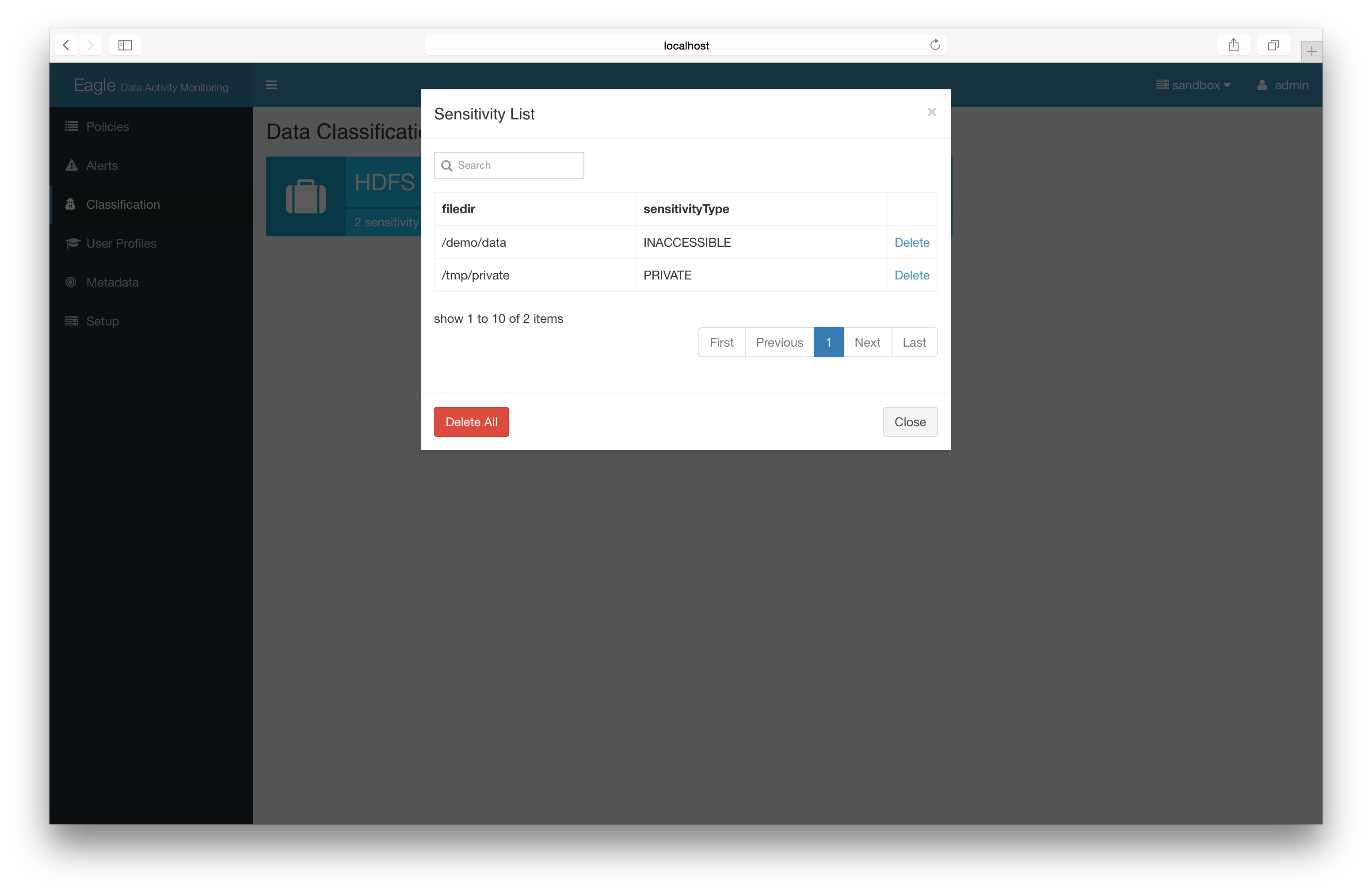
Advanced: delete lin batch
-
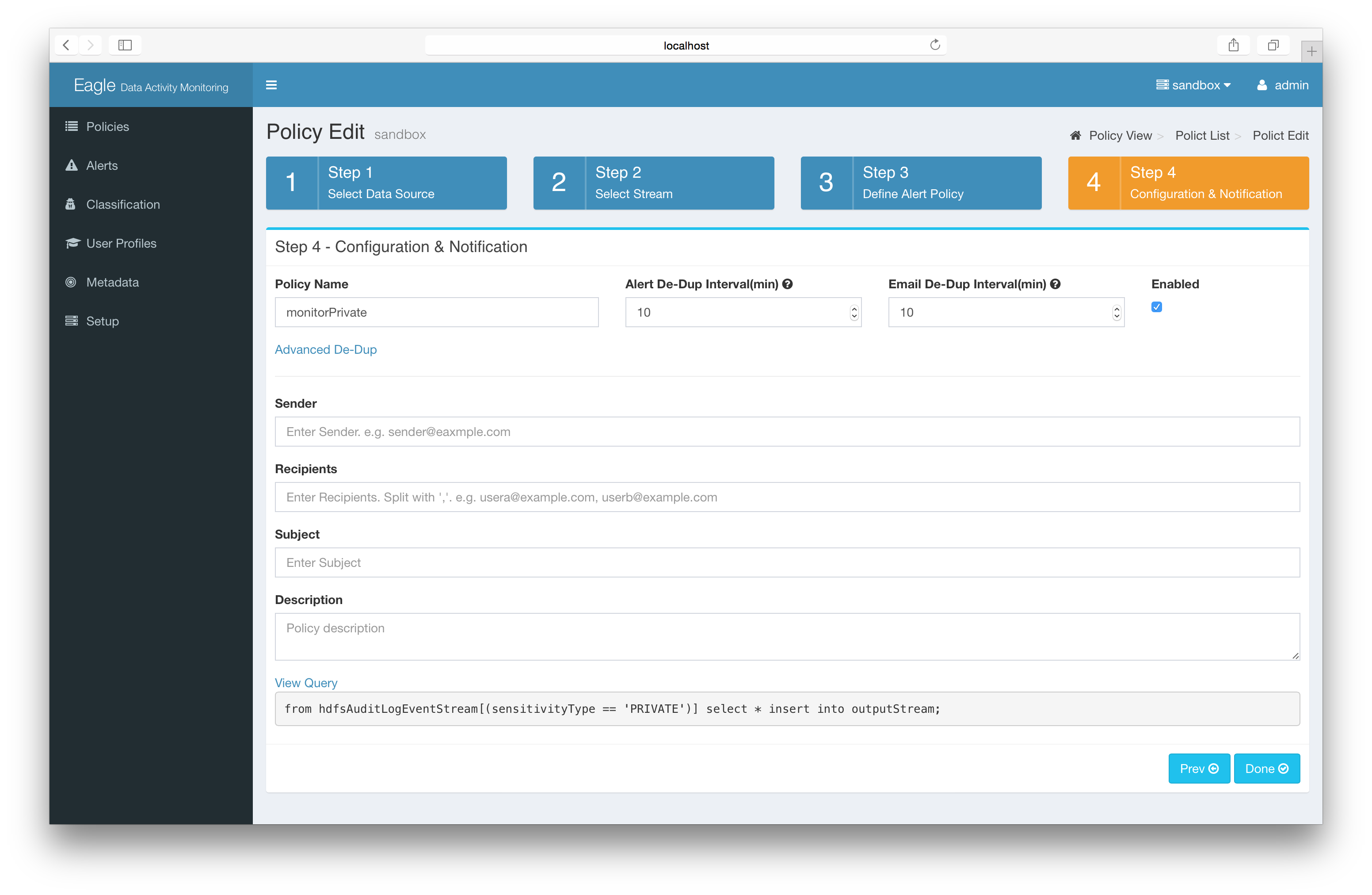
**Part 2: Monitor sensitive data
You can mark a particular folder/file as “PRIVATE”. Once you have this information you can create policies using this label.
For example: the following policy monitors all the operations to resources with sensitivity type “PRIVATE”.